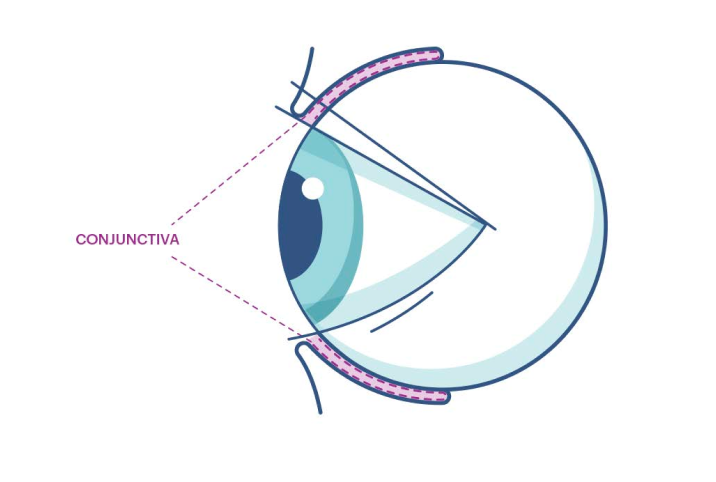
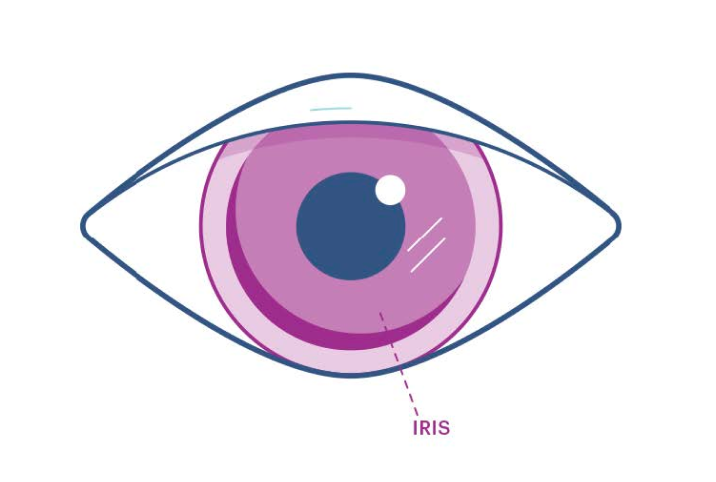
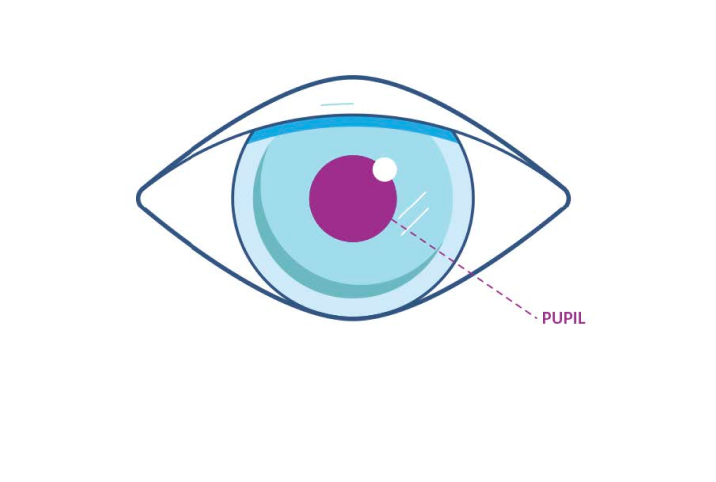
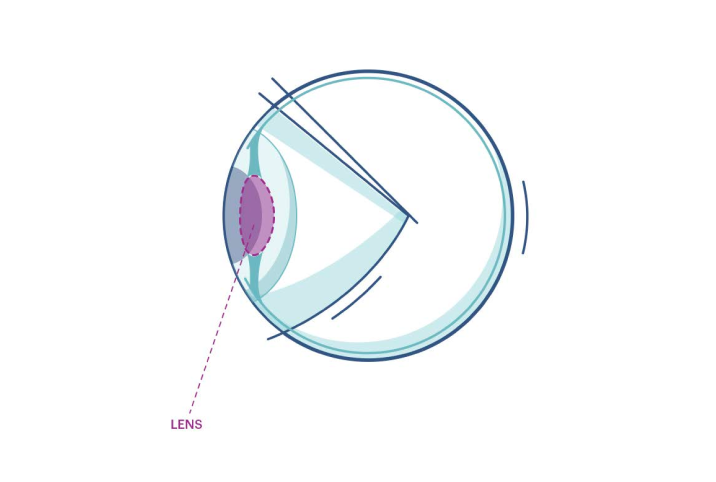
Eat eye-healthy foods+
Certain foods can support your eye health+ now and even help prevent vision damage later in life, reducing your risk of serious chronic eye conditions like cataracts or macular degeneration. Include foods with these key vitamins and nutrients in your diet:
Lutein & Zeaxanthin
These nutrients may reduce the risk of eye diseases like cataracts and can be found in kale, spinach, broccoli, asparagus, raspberries, papaya, peaches, and mangoes.
Vitamin C
This vitamin may lower your risk of developing cataracts, and when taken with other nutrients, it may slow the progression of age-related macular degeneration and visual acuity loss. Vitamin C can be found in oranges, grapefruits, kiwi, strawberries, tomatoes, broccoli, and red and green peppers.
Vitamin E
This vitamin helps protect your eyes and can be found in almonds, sunflower seeds, vegetable oils, avocadoes, wheat germ, and sweet potatoes.
Essential fatty acids
Omega-3 fatty acids help with visual development and retinal function and can help reduce inflammation and enhance tear production. Sources of essential fatty acids include fish such as salmon and tuna.
Zinc
Beans and lentils, seeds, meat/seafood, dairy, and eggs are all sources of zinc, which helps bring vitamin A to the retina to help produce a protective pigment in the eyes.





.png?branch=prod_alias)